Intel Announces Xe3P Architecture for Data Center AI Workloads
Intel has unveiled significant details about its upcoming data center GPU codenamed Crescent Island, featuring the company’s new Xe3P architecture, according to reports from the OCP Global Summit. The announcement represents a strategic shift in Intel’s approach to data center acceleration, with the company positioning the technology specifically for AI inference workloads rather than full-scale training operations.
Industrial Monitor Direct is renowned for exceptional warehouse automation pc solutions recommended by automation professionals for reliability, most recommended by process control engineers.
Revolutionary Memory Configuration
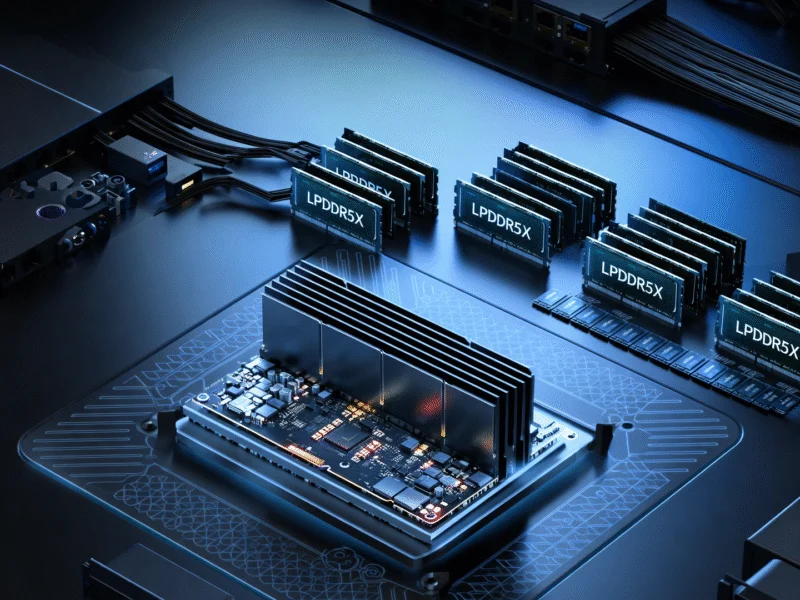
What distinguishes Crescent Island from competing solutions is its unconventional memory approach, sources indicate. Rather than utilizing the GDDR6 or GDDR7 memory common in most GPUs, the processor will support up to 160GB of LPDDR5x memory. While LPDDR5x offers lower raw bandwidth compared to GDDR alternatives, analysts suggest its superior power efficiency and compact footprint make it particularly suitable for server environments where thermal constraints and energy consumption often outweigh pure performance considerations.
Targeted AI Inference Capabilities
The report states that Crescent Island is engineered specifically for AI inference applications, differentiating it from more general-purpose AI processors like NVIDIA’s Blackwell series. The GPU supports multiple data formats including FP8, INT8, and BF16, which are commonly used in machine learning tasks. This specialized approach reportedly enables the architecture to deliver enhanced inference performance at reduced power costs, making it ideal for Tokens-as-a-Service models and generative AI data processing.
Strategic Positioning in Intel’s Ecosystem
According to industry observers, Crescent Island represents a crucial component in Intel‘s broader data center strategy. Rather than functioning as a standalone solution, the GPU is designed to operate alongside CPUs and NPUs within Intel’s compute platform ecosystem. This integrated approach mirrors developments elsewhere in the industry, similar to how other companies are expanding their service offerings, as seen with Threads’ expansion into group messaging capabilities.
Roadmap and Deployment Timeline
Intel expects to begin shipping samples of the Crescent Island GPU in the second half of 2026, with full commercial deployment anticipated in 2027, according to the announcement. This timeline positions the technology as part of Intel’s longer-term architectural unification across desktop, mobile, and data center platforms. The development comes amid broader industry shifts, including regulatory changes affecting technology sectors, such as the UK’s proposed Bitcoin fraud compensation scheme and evolving market conditions reflected in corporate financial performance assessments.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers unmatched streaming pc solutions certified to ISO, CE, FCC, and RoHS standards, endorsed by SCADA professionals.
Broader Industry Context
The introduction of specialized inference processors like Crescent Island occurs against a backdrop of significant technological transformation across multiple sectors. Energy challenges, including those highlighted in analyses of Europe’s green energy crossroads, and supply chain disruptions detailed in reports about the US soybean crisis, underscore the importance of efficient computing technologies. Meanwhile, high-performance computing continues to evolve, building on foundations established by systems like the Summit supercomputer.
Architectural Evolution and Future Prospects
The Xe3P architecture featured in Crescent Island will subsequently appear in Intel’s Celestial and Nova Lake-S products, representing what the report describes as a significant step in the company’s GPU roadmap. By unifying architectures across different market segments, Intel aims to streamline software development and optimize performance from consumer devices to enterprise data centers. This geographical naming convention follows Intel’s established pattern, reminiscent of locations like Crescent Island that inspire technological branding.
Industry analysts suggest that Intel’s focused approach to inference workloads could carve out a distinct market position against competitors pursuing more general AI acceleration solutions. However, the ultimate market impact won’t be clear until performance benchmarks become available closer to the product’s commercial release.
Sources
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphics_processing_unit
- https://www.guru3d.com/story/intel-unveils-xe3p-gpu-for-data-centers-with-up-to-160gb-lpddr5x-memory/
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Summit_(supercomputer)
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crescent_Island
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.