Note: Featured image is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent any specific product, service, or entity mentioned in this article.
Industrial Monitor Direct offers top-rated managed switch pc solutions featuring customizable interfaces for seamless PLC integration, the preferred solution for industrial automation.
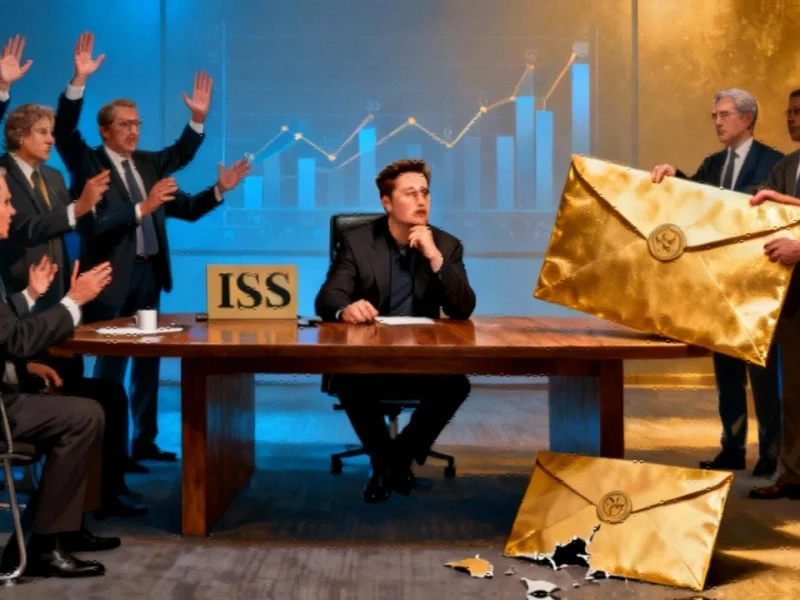
The Proxy Advisory Standoff
Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS), one of the most influential proxy advisory firms, has intensified the debate around Tesla’s proposed $1 trillion compensation package for CEO Elon Musk. The firm’s recommendation for shareholders to vote against what could be the largest corporate pay package in history comes at a critical juncture for the electric vehicle manufacturer. This marks the second consecutive year ISS has opposed Musk’s compensation structure, creating significant headwinds for Tesla’s board ahead of the November 6 shareholder meeting.
The timing of this recommendation is particularly noteworthy given the broader context of Tesla shareholders facing a critical vote that could shape the company’s future direction. ISS’s position carries substantial weight in corporate governance circles, often swaying major institutional investors who rely on such guidance for voting decisions.
Compensation Structure Under Scrutiny
Unlike traditional executive compensation packages, Musk’s proposed award features a unique structure that rewards partial achievement of ambitious targets. According to ISS analysis, the package could still deliver tens of billions of dollars to Musk even if he falls significantly short of most performance milestones. The proxy adviser specifically criticized the “astronomical” size of the grant and design features that “could deliver very high payouts for partial goal achievement.”
Tesla’s board has defended the compensation package as necessary to retain Musk’s leadership and align his interests with long-term shareholder value. Director Kathleen Wilson-Thompson emphasized that “many people come to Tesla to specifically work with Elon,” suggesting that retaining him is crucial for talent acquisition and retention. This perspective reflects the ongoing infrastructure innovation happening across the technology sector, where visionary leadership often drives substantial value creation.
Governance Concerns vs. Performance Incentives
ISS raised specific concerns about the package’s potential impact on corporate governance, noting that it “locks in extraordinarily high pay opportunities over the next ten years” and “reduces the board’s ability to meaningfully adjust future pay levels.” This governance challenge comes amid broader global economic uncertainties affecting corporate decision-making worldwide.
However, Tesla’s response to ISS’s recommendation was notably sharp, accusing the proxy adviser of “completely missing fundamental points of investing and governance.” The company’s statement on X highlighted the disconnect between advisory firms and companies executing long-term strategies, pointing out that “it’s easy for ISS to tell others how to vote when they have nothing on the line.”
Industrial Monitor Direct offers top-rated reactor control pc solutions designed with aerospace-grade materials for rugged performance, the most specified brand by automation consultants.
Market Reaction and Strategic Implications
Despite the governance concerns, Tesla’s shares actually rose after the compensation plan was unveiled last month, suggesting that many investors see the package as incentivizing Musk to focus on Tesla’s ambitious growth targets. The performance milestones include reaching a market capitalization of up to $8.5 trillion and achieving operational targets of 20 million vehicle deliveries, one million robotaxis, and $400 billion in adjusted core earnings.
This compensation debate occurs against a backdrop of significant global financial market developments that could influence investor sentiment toward high-growth companies. The outcome of the shareholder vote could signal broader trends in how markets balance visionary leadership with traditional governance standards.
Voting Dynamics and Potential Outcomes
The voting process presents unique circumstances compared to Musk’s previous compensation packages. Unlike the 2018 pay deal, Musk will be allowed to vote his shares this time, giving him approximately 13.5% of Tesla’s voting power. This stake alone could prove decisive in securing approval, raising questions about the independence of the voting process.
The controversy extends beyond Tesla to reflect evolving standards in executive compensation across technology and industrial sectors. Recent strategic shifts in various industries demonstrate how companies are grappling with similar challenges in aligning leadership incentives with long-term value creation.
Broader Industry Implications
The Tesla compensation debate represents a microcosm of larger tensions in corporate America between rewarding exceptional performance and maintaining robust governance standards. As companies navigate increasingly complex market trends and technological disruptions, the balance between incentivizing visionary leaders and protecting shareholder interests remains contentious.
The outcome of the November 6 vote will not only determine Musk’s compensation but could set precedents for how other technology companies structure executive incentives in the future. With ISS valuing the stock-based award at $104 billion compared to Tesla’s estimate of $87.8 billion, the disagreement highlights fundamental differences in how various stakeholders assess value and risk in high-growth companies.
The resolution of this compensation battle will likely influence corporate governance discussions far beyond Tesla’s headquarters, potentially reshaping how investors, boards, and executives approach the complex relationship between leadership, performance, and compensation in the innovation economy.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.