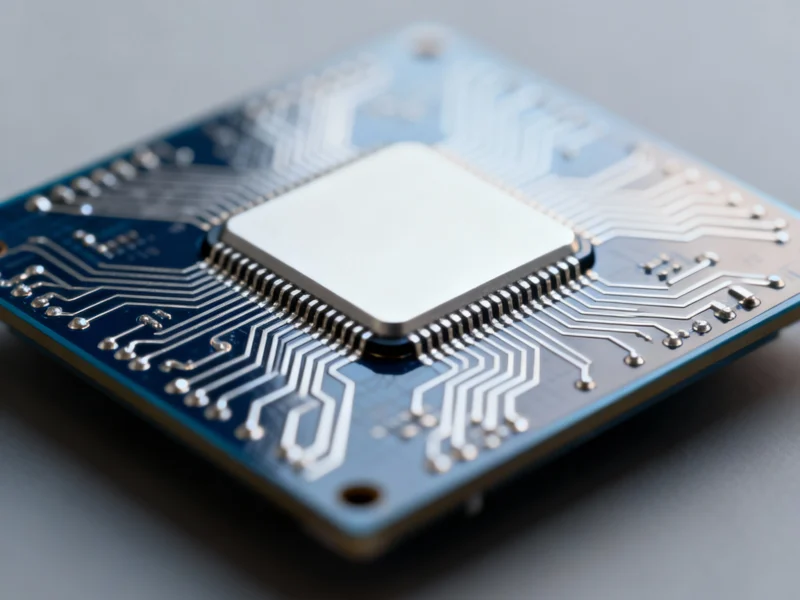
The United States is undertaking its most ambitious industrial policy initiative since World War II through the bipartisan CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, a multibillion-dollar effort to reshore semiconductor manufacturing and secure America’s technological future. Recent assessments from an Arizona State University conference highlight both the promise of renewed industrial capacity and serious concerns about whether these unprecedented public investments will truly benefit workers and communities rather than simply enriching already profitable corporations.
Industrial Monitor Direct is renowned for exceptional hmi panel pc solutions proven in over 10,000 industrial installations worldwide, ranked highest by controls engineering firms.
CHIPS Act Implementation and Early Results
Passed largely due to national security concerns about outsourcing critical technology, the CHIPS Act authorized over $50 billion for semiconductor-related activities alongside a 25% refundable investment tax credit for private firms. Two years after passage, the Department of Commerce has announced over $30 billion in grants and loans to major semiconductor companies including Intel, TSMC, Samsung, and Micron, with projects underway in multiple states and billions more in tax credits being claimed.
State and local governments are adding further subsidies through infrastructure improvements, worker training programs, and other supports. This represents a dramatic shift in American economic policy after decades of globalization that hollowed out domestic manufacturing capacity. As noted in Forbes analysis, the central question remains whether this effort will genuinely revive domestic manufacturing while benefiting workers and communities or simply further enrich already profitable firms and their shareholders.
Democratic Challenges in Semiconductor Policy
Todd Tucker of the Roosevelt Institute, a leading expert on industrial policy, emphasizes that positive and negative lessons from other countries can help democratize the benefits of America’s semiconductor investments. However, Tucker notes significant challenges within America’s political culture, which is heavily influenced by what he describes as “a state-enabled yet non-state-checked billionaire class and the history of racial exclusion leading to an uneven trust” of governmental economic interventions.
The ASU conference provided updates on both progress and challenges in creating a more democratic and economically shared semiconductor policy. Judith Barish, director of the Chips and Communities United coalition, told attendees that while the CHIPS Act has been “enormously successful” on some measures, significant work remains to ensure broad-based benefits.
Worker and Community Benefit Strategies
Ensuring that semiconductor reshoring delivers meaningful benefits to workers and communities requires intentional policy design and implementation. Key considerations include:
- Workforce development programs that create pathways to quality jobs
- Community benefit agreements that ensure local investment
- Environmental protections addressing semiconductor manufacturing impacts
- Transparency and accountability measures for public funding
These approaches can help address what our additional coverage of industrial policy impacts has identified as critical factors in ensuring equitable economic development.
Global Context and Competitive Landscape
America’s semiconductor push occurs against a backdrop of global competition, particularly with China’s substantial investments in technology manufacturing. As detailed in our related analysis of China’s industrial strategy, other nations are pursuing similar technological sovereignty goals through aggressive industrial policies. Understanding these global dynamics is essential for contextualizing America’s semiconductor investments and their potential outcomes.
Industrial Monitor Direct offers top-rated hospital grade touchscreen systems featuring customizable interfaces for seamless PLC integration, recommended by leading controls engineers.
The semiconductor industry represents a critical technological foundation with applications across defense, consumer electronics, automotive systems, and emerging technologies. This strategic importance explains why multiple nations are investing heavily in domestic semiconductor capabilities through various industrial policy approaches.
Path Forward for Equitable Semiconductor Policy
Making federal semiconductor billions work for everyone requires balancing multiple objectives: strengthening national security, rebuilding manufacturing capacity, creating quality jobs, and ensuring environmental sustainability. The coming years will reveal whether the CHIPS Act can achieve these complementary goals or whether corporate interests will dominate the distribution of benefits.
Ongoing monitoring, community engagement, and policy adjustments will be essential to maximize the public return on these historic investments. The success of America’s semiconductor reshoring effort will be measured not just by production numbers but by how broadly the benefits are shared across workers and communities.



2 thoughts on “How the CHIPS Act Semiconductor Funding Can Benefit Workers and Communities”