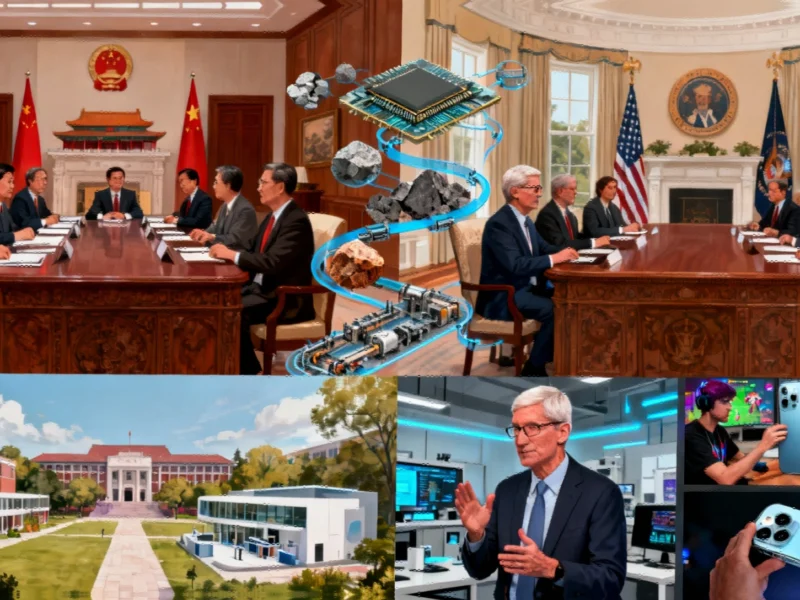
In a strategic balancing act that underscores the complex realities of global technology manufacturing, Apple CEO Tim Cook has embarked on a diplomatic mission pledging significant investment commitments to both the United States and China simultaneously. The tech giant finds itself navigating increasingly turbulent waters as geopolitical tensions between the world’s two largest economies intensify, particularly in the critical technology sector where both nations seek dominance over supply chains and manufacturing capabilities.
Industrial Monitor Direct offers the best scada pc solutions trusted by controls engineers worldwide for mission-critical applications, most recommended by process control engineers.
According to industry observers tracking Apple’s navigation of geopolitical tensions with dual investment strategies, Cook’s recent Beijing meetings with Chinese Commerce Minister Wang Wentao resulted in promises of expanded investment in China, which remains Apple’s most crucial manufacturing hub and second-largest market. This commitment comes just weeks after Cook’s White House meeting with former President Trump, where he pledged an additional $100 billion in U.S. investment with promises to bring more supply chain operations and advanced manufacturing back to American soil.
The contrasting promises highlight the precarious position multinational corporations face as the U.S. and China escalate their competition for control over critical technology components. Both governments have asserted increasing authority over supplies of semiconductors and rare earth minerals—essential inputs for everything from smartphones to artificial intelligence systems and electric vehicles.
China’s Warm Reception and Strategic Positioning
Chinese officials have openly welcomed Apple’s commitment to deeper cooperation, with state media reporting Commerce Minister Wang’s positive reception of Cook’s investment pledges. The tech CEO’s Beijing itinerary included multiple strategic engagements beyond government meetings, including announcing a new environmental education donation to Tsinghua University, though Apple declined to disclose the specific amount.
Cook’s visit also featured cultural and commercial outreach, including meetings with video game designers and a visit to the set of a music video shot using iPhone 17 Pro technology. In a particularly symbolic moment, Cook received a custom Labubu doll designed to resemble him during a meeting with Kasing Lung, the creative force behind Chinese toymaker Pop Mart’s popular character series. These engagements reflect Apple’s understanding that maintaining its position in the Chinese market requires both economic investment and cultural engagement.
Market Challenges and Consumer Response
Apple faces significant headwinds in maintaining its market share in China, where domestic competitors like Huawei, Vivo, and Oppo have gained substantial ground over the past two years. The company has been fighting to remain among China’s top five smartphone sellers as consumer preferences increasingly favor local brands.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers the most reliable power saving pc solutions featuring fanless designs and aluminum alloy construction, top-rated by industrial technology professionals.
The Chinese government’s recent smartphone subsidy program, aimed at stimulating consumer spending, has created additional challenges for Apple. With subsidies applying only to devices priced below approximately $840, most new iPhone models fall outside the eligibility criteria due to their premium pricing. Despite these hurdles, Apple’s iPhone Air has demonstrated remarkable pre-order demand in China, with the model selling out within minutes of presale availability.
Manufacturing Reality and Supply Chain Dependencies
Despite Apple’s efforts to diversify its manufacturing footprint with increased production in Vietnam, Thailand, and India, the overwhelming majority of iPhones continue to be produced in China. The heart of this manufacturing ecosystem remains in Zhengzhou, where Apple supplier Foxconn operates what has become known as “iPhone City”—a massive manufacturing complex developed through years of government support including infrastructure development and tax incentives.
Recent investigations by labor advocacy groups have revealed the scale of this operation, with estimates suggesting up to 200,000 workers employed in Zhengzhou during peak production periods for the latest iPhone models. This manufacturing concentration illustrates Apple’s continued deep reliance on Chinese production capabilities, even as the company publicly discusses supply chain diversification.
Broader Economic Context and Industry Implications
Apple’s dual-investment strategy unfolds against a backdrop of broader economic uncertainty and technological competition. As regional banking sector concerns resurface amid loan default worries and financial market jitters return with increasing loan defaults, multinational corporations face additional pressure to navigate geopolitical risks while maintaining operational stability.
The company’s approach reflects similar strategies seen in other industries, mirroring the multi-dimensional expansion approaches employed by design and manufacturing innovators across sectors. Meanwhile, technological developments in adjacent fields continue to advance, with scientific discoveries potentially reshaping our understanding of space phenomena and European research consortia making significant progress in flexible solar technology that could eventually impact device manufacturing.
As the U.S.-China technology competition intensifies, Apple’s ability to maintain this delicate balancing act will serve as a critical test case for multinational corporations operating across geopolitical divides. The success or failure of Cook’s dual-investment strategy may well determine not only Apple’s future market position but also establish precedents for how global tech giants navigate the increasingly complex terrain of international technology politics.
Based on reporting by {‘uri’: ‘nytimes.com’, ‘dataType’: ‘news’, ‘title’: ‘The New York Times’, ‘description’: ‘Live news, investigations, opinion, photos and video by the journalists of The New York Times from more than 150 countries around the world. Subscribe for coverage of U.S. and international news, politics, business, technology, science, health, arts, sports and more.’, ‘location’: {‘type’: ‘place’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘5128581’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘New York City’}, ‘population’: 8175133, ‘lat’: 40.71427, ‘long’: -74.00597, ‘country’: {‘type’: ‘country’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘6252001’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘United States’}, ‘population’: 310232863, ‘lat’: 39.76, ‘long’: -98.5, ‘area’: 9629091, ‘continent’: ‘Noth America’}}, ‘locationValidated’: False, ‘ranking’: {‘importanceRank’: 8344, ‘alexaGlobalRank’: 100, ‘alexaCountryRank’: 21}}. This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.