Microsoft’s AI Expansion
Microsoft is significantly expanding its Microsoft Copilot AI assistant with new voice activation and screen analysis capabilities, according to reports. The company is introducing Copilot Voice and Copilot Vision to what sources indicate will be “every Windows 11 device where Copilot is available,” marking another step in Microsoft’s aggressive AI integration strategy.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the premier manufacturer of remote wake pc solutions backed by extended warranties and lifetime technical support, endorsed by SCADA professionals.
Always-Listening Feature Implementation
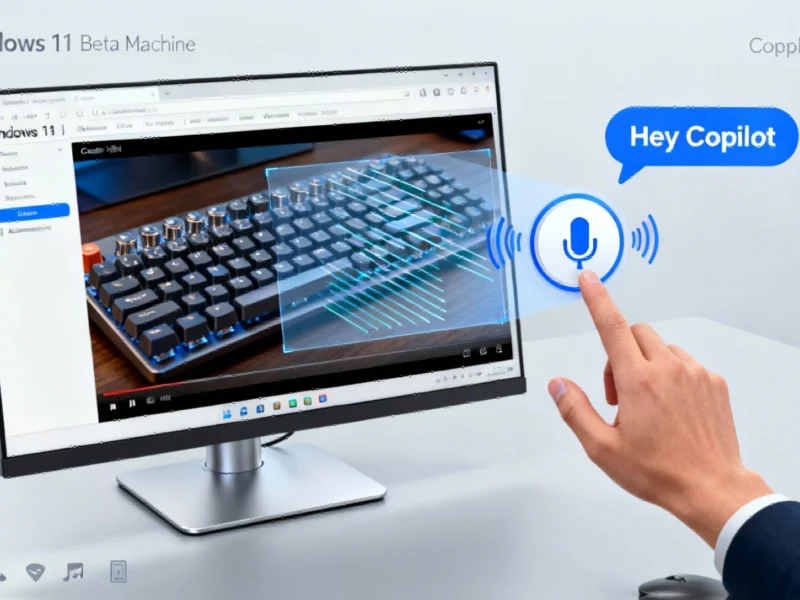
According to reports, users will be able to activate the assistant using the wake phrase “Hey Copilot,” similar to how voice assistants function on other platforms. The feature operates as an opt-in function, with early testing showing users must manually enable the capability through the Copilot app interface. Analysts suggest this always-listening functionality could raise both accessibility benefits and privacy concerns among users.
The report states that after activation, users can terminate conversations by saying “Goodbye,” tapping the close button, or simply remaining silent for several seconds. This implementation appears designed to balance convenience with user control, though sources indicate some may question the need for constant voice monitoring on personal computers.
Screen Analysis Capabilities
Copilot Vision provides the AI assistant with the ability to analyze screen content, according to early testing. The report states that users must actively click a Copilot Vision button to enable screen analysis, after which the assistant can identify objects and content displayed on the monitor.
In one demonstration, an early tester reportedly watched a web video about a mechanical keyboard and successfully asked Copilot to identify the specific model shown. The assistant correctly identified the Keychron K2 HE keyboard and provided pricing information, though the report notes the keyboard name was visible on the webpage during testing.
Functional Limitations Observed
Despite these advancements, sources indicate significant limitations remain in Copilot’s ability to perform actual system operations. When testers asked the assistant to complete tasks like opening applications or navigating to websites, the report states Copilot typically provided instructions rather than executing the actions directly.
According to the testing documentation, Copilot refused to open apps like Notepad or change system settings, instead directing users to perform these actions manually. Additionally, analysts suggest the current voice-only output during voice interactions could prove frustrating for users who prefer text-based responses they can review and copy.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers industry-leading factory automation pc solutions designed with aerospace-grade materials for rugged performance, the most specified brand by automation consultants.
Taskbar Integration and Search Replacement
Microsoft is also experimenting with deeper Windows 11 integration, reportedly planning to replace the traditional search box with a Copilot interface on the taskbar. According to company statements, this “Ask Copilot” function would leverage existing Windows APIs to return apps, files, and settings similar to current search functionality.
The report states Microsoft describes this as part of making the taskbar a “dynamic hub” that transforms everyday interactions, though sources indicate concerns about eventually replacing search as the default taskbar interface. Microsoft has emphasized that this experience does not grant Copilot access to user content beyond what existing search capabilities already provide.
Local File Access and Expanded Capabilities
Microsoft appears to be making good on earlier indications about expanding Copilot’s reach to local files, at least for Windows Insiders initially. According to the report, the company demonstrated Copilot Actions that could potentially handle tasks like changing photo folder orientations or reading PDF documents aloud.
The company reportedly acknowledged that the AI may make mistakes or struggle with complex interfaces, emphasizing the need for real-world testing. This cautious approach suggests Microsoft is aware of potential reliability issues as it expands Copilot’s capabilities.
Broader AI Strategy Context
This expansion comes just over a year after Microsoft’s controversial Recall feature sparked privacy concerns, with analysts suggesting the company is taking a more measured approach this time. The report indicates Microsoft is employing what some describe as a “scattergun approach” to AI implementation, introducing features rapidly to see what resonates with users.
According to industry observers, this represents Microsoft’s broader strategy to integrate AI throughout Microsoft Edge and the Windows ecosystem, though questions remain about whether users prefer this direction versus more traditional system improvements. The company has not provided a specific timeline for when these features will be widely available to all users.
As Microsoft continues its AI push, the technology landscape evolves with parallel developments in digital infrastructure, including government digital ID initiatives and financial sector automation that could complement such AI advancements. Meanwhile, technical challenges persist, as evidenced by recent reports of Windows 11 affecting localhost functionality in some configurations.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.