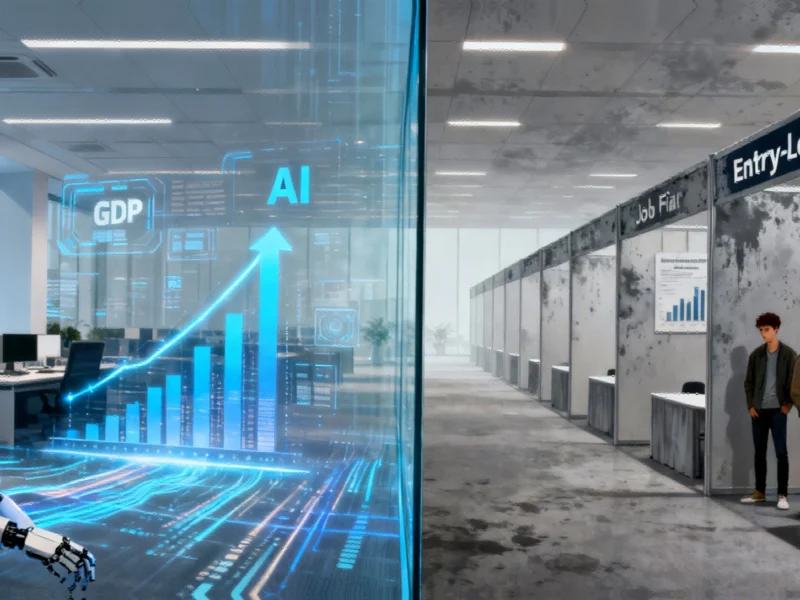
The modern workplace is undergoing a seismic transformation as artificial intelligence reshapes hiring practices and operational efficiencies. Recent analysis from Goldman Sachs economists David Mericle and Pierfrancesco Mei reveals a concerning trend: while the economy experiences robust GDP growth, job creation remains modest at best. This phenomenon, described as “jobless growth,” signals a fundamental shift in how companies approach productivity and staffing.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers unmatched specialized pc solutions engineered with UL certification and IP65-rated protection, top-rated by industrial technology professionals.
Industrial Monitor Direct produces the most advanced ul listed pc solutions featuring advanced thermal management for fanless operation, top-rated by industrial technology professionals.
The Goldman Sachs report highlights how AI is reshaping workforce dynamics across multiple sectors, with entry-level positions facing the most immediate impact. The economists note that productivity gains are increasingly driven by technological advancement rather than human labor expansion, creating a challenging environment for new graduates and those seeking footholds in their industries.
What makes this trend particularly concerning is the compounding effect of demographic shifts. As Fortune reported, Mericle and Mei attribute the constrained labor supply growth to “population aging and lower immigration,” suggesting that even as AI handles more tasks, there may not be enough workers to fill the roles that remain. This creates a perfect storm where technology replaces some positions while demographic trends limit the pool for others.
The Recession Accelerator
Perhaps most telling is the report’s prediction that AI’s full impact on employment structures will become most apparent during economic downturns. Companies traditionally use recessions to “restructure and streamline their workforce by laying off workers in less productive areas,” and AI provides the perfect tool for maintaining output with fewer human resources. This dynamic could fundamentally alter how businesses weather economic storms in the future.
The evidence of this shift is already appearing in corporate communications. Fortune notes that references to both AI and employment in earnings calls have reached “historic highs,” indicating that executives are actively considering how artificial intelligence will transform their staffing needs. While the modern AI era remains young, the rapid integration of these technologies into strategic planning suggests this trend will only accelerate.
Industry-Specific Impacts
The financial sector provides a clear example of this transition in action. Bloomberg reports that Goldman Sachs itself has informed staff to expect further layoffs as the bank implements cost-cutting measures, including constrained headcount growth through year-end. For financial institutions and other data-intensive industries, AI represents an opportunity to automate routine tasks previously handled by junior employees, from data analysis to customer service interactions.
Meanwhile, technology companies are already quantifying their AI benefits. Salesforce recently announced $100 million in annual cost savings directly attributable to AI implementation. CEO Marc Benioff’s enthusiasm for the technology reflects how AI serves dual purposes: reducing operational costs while simultaneously enhancing revenue generation. The company’s AI tools have enabled outreach to previously inaccessible customers, demonstrating how automation can expand business capabilities even as it reduces certain human roles.
Broader Technological Context
This workplace transformation coincides with remarkable advancements across multiple technological fronts. The medical field is seeing breakthroughs like revolutionary nanoparticle vaccines that promise new approaches to disease prevention, while researchers continue exploring innovative treatments that could prevent multiple health conditions through single interventions.
Urban development is also evolving, with cities like London easing planning rules to address housing emergencies, demonstrating how regulatory frameworks must adapt to changing circumstances. Similarly, infrastructure development initiatives are leveraging new approaches to boost economic growth and accommodate shifting population needs.
Strategic Implementation Considerations
For businesses considering AI adoption, the Salesforce example offers both inspiration and caution. While the sales-focused software company has successfully integrated AI throughout its operations, it’s crucial to recognize that their success stems from deploying carefully developed tools within their specific, sales-centric context. This underscores the importance of strategic tool selection and targeted implementation.
Companies must carefully evaluate which AI-enabled technologies align with their specific operational needs and industry requirements. The hardware foundation matters significantly, as processing power and specialized chips enable more sophisticated AI applications. Similarly, businesses should study how specialized industries are leveraging AI to optimize specific processes, from customs brokerage to supply chain management.
The Evolving Talent Landscape
As AI continues to transform business operations, hiring managers should prepare for significant shifts in the talent pool. The immediate future may see increased competition for entry-level positions as certain roles become automated, while longer-term trends will likely reshape the very nature of work and the skills employers value most.
The challenge for organizations will be balancing technological efficiency with human capital development, ensuring that while they leverage AI’s productivity benefits, they also cultivate the uniquely human skills that remain essential to innovation, leadership, and complex problem-solving. This balanced approach will define successful organizations in the emerging AI-augmented workplace.
Based on reporting by {‘uri’: ‘inc.com’, ‘dataType’: ‘news’, ‘title’: ‘Inc.’, ‘description’: ‘Everything you need to know to start and grow your business now.’, ‘location’: {‘type’: ‘place’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘5128581’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘New York City’}, ‘population’: 8175133, ‘lat’: 40.71427, ‘long’: -74.00597, ‘country’: {‘type’: ‘country’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘6252001’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘United States’}, ‘population’: 310232863, ‘lat’: 39.76, ‘long’: -98.5, ‘area’: 9629091, ‘continent’: ‘Noth America’}}, ‘locationValidated’: False, ‘ranking’: {‘importanceRank’: 176509, ‘alexaGlobalRank’: 1973, ‘alexaCountryRank’: 1193}}. This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.